ErlanggaBlog.com – There are many types of nasal cancer. The paranasal sinuses, or small hollow spaces around the nose, are the most common. Nasal cancer occurs in the paranasal sinuses, and the sinuses are usually not symptomatic, but can be dangerous. Other forms of nasal cancer are melanoma, a type of skin cancer that invades the base of the skull and spreads throughout the body.
Tumor removal surgery is the most common treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer
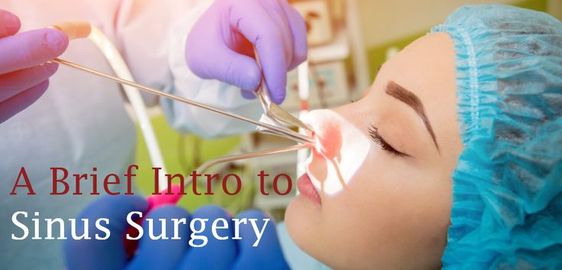 Treatment for nasal cancer varies by stage. Surgical removal of the tumor is the most common treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer. However, this surgery isn’t always possible, and can require a neck dissection if it has spread throughout the body. Elective neck interventions are more common when the tumor has spread to other parts of the body. In such cases, patients may require radiation or surgery. However, the type of treatment will depend on the extent of the cancer.
Treatment for nasal cancer varies by stage. Surgical removal of the tumor is the most common treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer. However, this surgery isn’t always possible, and can require a neck dissection if it has spread throughout the body. Elective neck interventions are more common when the tumor has spread to other parts of the body. In such cases, patients may require radiation or surgery. However, the type of treatment will depend on the extent of the cancer.
A biopsy is a way to confirm a diagnosis of sinus cancer. It involves the removal of a piece of tissue with a surgical knife. This procedure may be done under topical or general anaesthesia. During a laryngoscopy, a lighted tube with a camera looks into the larynx and voice box to look for any abnormalities. While an incision biopsy requires stitches, a needle biopsy may result in bleeding. Incision biopsy may require stopping blood thinners prior to the procedure.
The symptoms of nose and sinus cancer are unlike any other type of cancer
In many cases, the symptoms of nasal and sinus cancer are similar to symptoms of other common conditions. Unlike other types of cancer, they are unlikely to be caused by the disease itself. Your GP may refer you to a specialized doctor for further investigation. Your doctor may request tests, such as a CT scan, MRI, PET scan, and ultrasound. During the course of the diagnosis, you will undergo a number of tests to determine the exact type of cancer.
The incidence of nasal cavity malignancy depends on several factors, including age and sex. Age, TNM staging, tumor grade, and survival time are considered. The type of treatment also influences survival. In this study, a national cancer database was used to determine the overall survival and prognostic factors for nasal cavity cancer. These factors can help you choose the most effective treatment for your specific condition. For more information, visit the National Cancer Database
MRI is a very good tool for identifying tumors
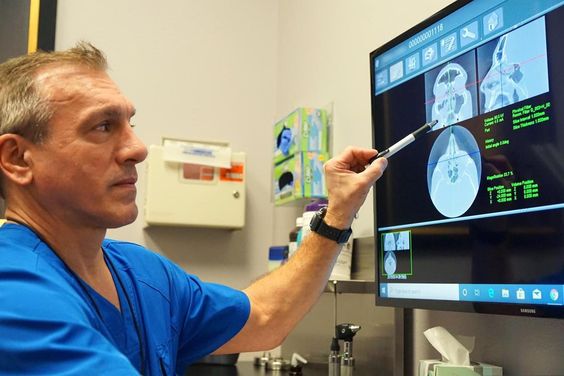
MRIs and CT scans are also used to detect nasal cancer. CT scans are an important component of treatment for nasal cancer. MRIs are excellent tools for identifying tumors and analyzing their spread. They are also useful for staging the cancer. A MRI can also provide fine anatomic detail. A rods lens endoscope biopsy is often performed under topical anesthesia. If the doctor suspects that the disease has spread, he will use the latest techniques to diagnose and treat the condition.
While the exact cause of nasal and sinus cancer is unknown, damage to cells’ DNA may play a role. Damage to the DNA of cells causes cancer cells to reproduce more rapidly than healthy ones. Tobacco and smoking irritate cells in the nasal cavity. Middle-aged men are more susceptible to nasal and sinus cancer. Workplace environments may aggravate the sensitive lining of the nose and sinuses. There has been a connection between nasal and sinus cancer and the human papilloma virus.
CT scans use x-rays to produce detailed cross-sectional images. They are particularly useful for nasal cancer because they show the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to lymph nodes. Moreover, they can show whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, including the lungs. The CT scan can also identify the location of the tumor as well as its extent. However, CT scans are not diagnostic tests and should not be used as the only method for diagnosis.
Radiotherapy is generally associated with a lower survival rate
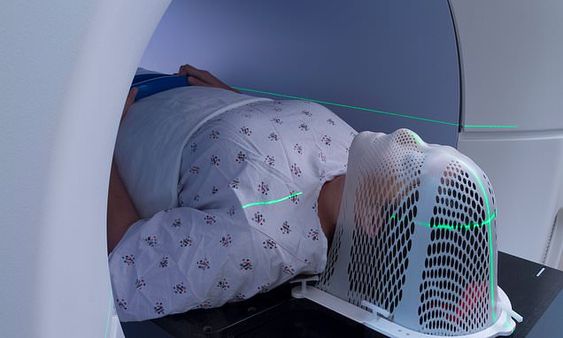
The survival rate of patients diagnosed with nasal cavity cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the spread to the surrounding structures, the response to chemotherapy, and the treatment. Radiotherapy is generally associated with lower survival rates for T2 lesions, but is still an effective way to treat nasal cancer. Moreover, it reduces the risk of recurrence and helps prevent the spread of the cancer. In addition, radiotherapy is a significant factor in determining overall survival.
A doctor may perform a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before the surgery to determine the extent of the cancer. This test is usually done to assess the location of the cancer in the neck region, but can also show the extent of the disease. If the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, the doctor may also remove them in addition to the tumor. If the radiation is unsuccessful, the tumor may spread throughout the body. This type of surgery is not suitable for all patients with nasal cancer.







